Search Engine Indexing: A Beginners Guide
What is Search Engine Indexing?
Search engine indexing is the process of discovering, storing, and organizing web page content so that it can be easily & quickly searched, analyzed, and retrieved by search engines. In other words, it is the process that search engines such as Google, Bing, and Yahoo use to crawl and index web pages and their content.
For example, when you type into Google "site:[yourdomain.com]" where you replace [yourdomain.com] with your domain, you'll see all of the pages of that domain that are currently indexed in Google:
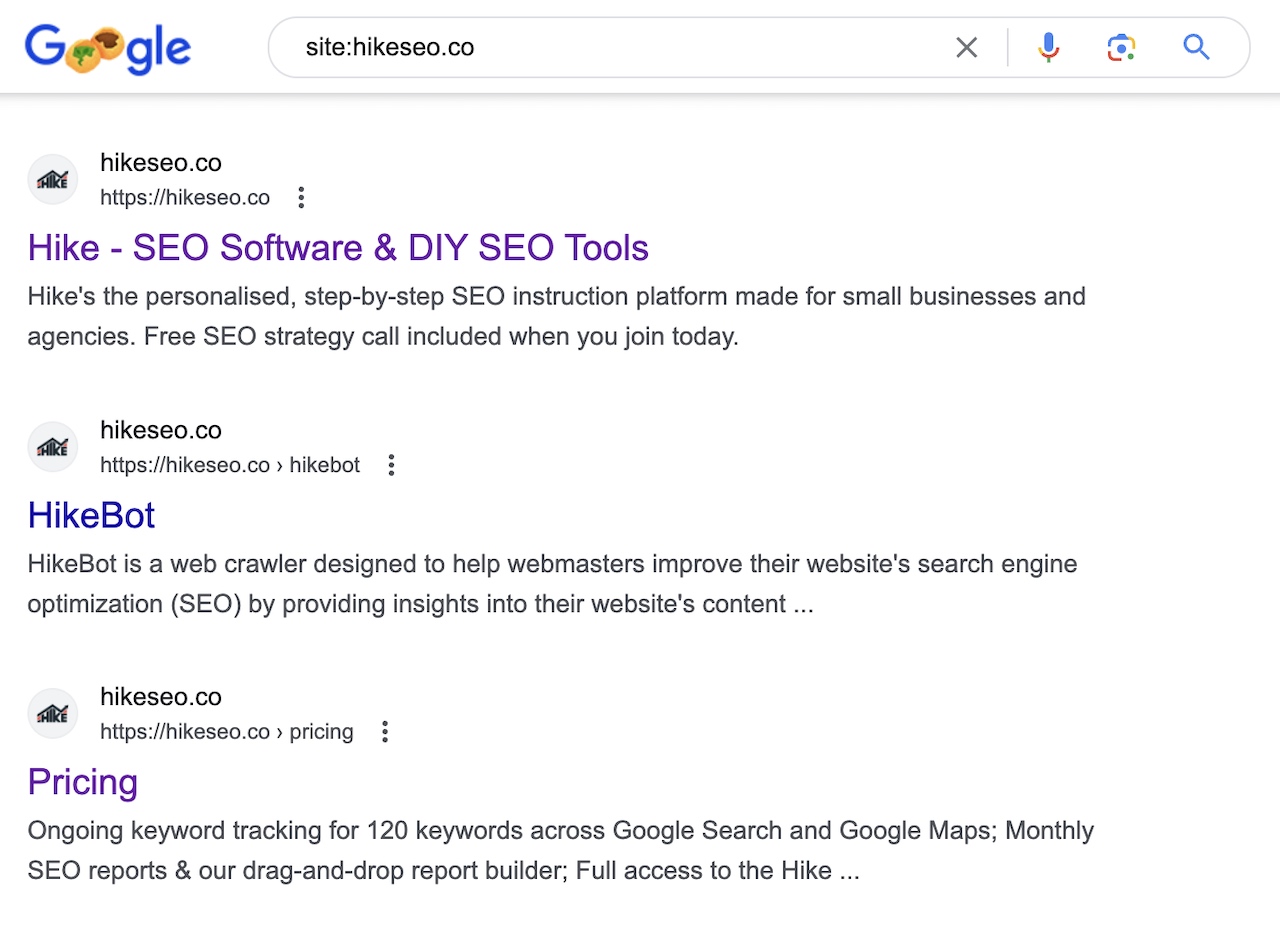
Why Do Search Engines Need To Index Pages?
Just as a dictionary is organized to allow you to easily and quickly find a definition of a word, search engines index pages so they can serve relevant and useful search results to users. The search engine uses its expansive index to quickly search through all the relevant web pages to find those that are most likely to answer the user's question or fulfill their search intent.
Without using an index, search engines would have to search through every single web page on the internet every time a user entered a search query. This would be an incredibly slow and inefficient process, because there are billions of web pages on the web, and therefore wouldn’t be able to provide the high-quality search experience that users expect.
The Three Processes of Search Engines
A search engine has three main processes it uses to serve relevant results to its users:
What is a Search Engine Index?
A search engine index is a massive database or library of information that contains information about all the web pages that the search engine has crawled and analyzed over time that allows search engines to quickly and efficiently respond to user search queries by providing a list of relevant web pages.
When a user enters a search query into the search engine, it searches through its index to find pages that are relevant to the query and then ranks them based on factors within its complex algorithm, including more general factors such as relevance, authority, and popularity.
Ways How Search Engines Can Easily Index Your Website
There are several ways how search engines can use to index your website, so it’s important to make sure they are understood and implemented on your website:
XML Sitemaps
By having an XML sitemap available & updated, search engines can quickly find all of the current live pages on your website, so they can easily crawl and index them. Most CMS platforms automatically create and update an XML sitemap, however, if you have a custom platform that doesn’t have this functionality, it’s important to create a sitemap and keep it updated whenever pages are created, updated, or deleted.
Google Search Console (GSC)
GSC Sitemap Submission
GSC has the function to submit your XML sitemap or sitemap index so that it knows where to find it on your website if it’s not in a common location, like in a CMS. Follow these simple steps to submit your sitemap or sitemap index within GSC.
You'll see in the screenshot below that Hike has submitted their XML sitemap index file to Google Search Console:

GSC URL Inspection Tool
You can request indexing or reindexing of a specific URL, however, indexing can take up to a week or two, so you can check the progress within this tool.
There are two steps involved, as per the GSC help page:
- 1Inspect the page URL
- 2Click on Request indexing on the inspection result page for the URL
Robots Meta Tag
By default, unless otherwise specified, a public page is automatically indexed. There may be circumstances where certain pages should not be indexed, for example, if it’s a marketing or advertising landing page or a private access page that only those with a direct link to it can access. In these cases, a robots meta tag can be added to each of these pages to let search engine bots know that you don’t want these pages to be indexed.
Below is an example of the robots.txt file for hikeseo.co. The asterisk (*) wildcard assigns directives to every user-agent, which applies the rule for all bots. Therefore in this example, the /wp-admin/ page is not to be crawled at all, whereas the /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php page can be crawled by every bot.

You would put this tag into the head section of the HTML, however, many CMS platforms have SEO plugins that have a noindex option to choose from, so you most likely don’t need to manually add it yourself:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">
Robots.txt
The robots.txt file can have rules to specify which directories or pages to crawl or not to crawl, however, it doesn’t on its own prevent a page from being indexed. The disallow directive tells search engine bots not to crawl a specific area of the website, but if that page or directory of pages already is indexed or is within the sitemap, then it could still be indexed. That’s why it’s important to also use the Robots Meta Tag on pages you don’t want indexed to ensure it doesn’t show up in search results.
It’s also important to have an XML sitemap reference in the robots.txt file so web crawlers can easily find your website’s sitemap. For example, you would add at the top of the robots.txt file the following snippet, replacing the exact URL to the sitemap with yours:
Sitemap: http://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
Alternative Search Engine Consoles
Search engines other than Google have their consoles where you can submit your website sitemaps and submit pages for indexing. Below are a few of the main ones:
Bing
Submitting a sitemap on Bing is very simple, and it also allows you to resubmit it if you’ve had recent changes within it. Here’s a quick guide from Bing Webmaster Tools.
Bing’s URL submission tool allows you to submit one or more URLs and after submission, the URLs are immediately evaluated for search indexation. There’s a maximum daily quota, so if you max this out, then you’ll need to wait until the next day to add more URLs. Here’s how to submit URLs for indexing in Bing.
Yandex
Submitting a sitemap on Yandex takes only a minute, by following these steps:
- 1Go to the Sitemap files section
- 2Choose the site from the list
- 3Enter the XML sitemap file URL
- 4Click the Add button
To make sure that changes that are made on your website are updated faster in Yandex search results, you can notify the indexing robot by following these steps:
- 1In Yandex Webmaster, go to Indexing → Reindex pages
- 2Enter the URL of the updated page in the field
- 3Click Send
Common Search Engine Indexing Questions
You may have other questions in regards to indexing, that may be answered in the below common questions:
How To Get Your Website Indexed Faster?
Firstly, make sure the basics are in place, such as the XML sitemap, and have the sitemap referenced in the robots.txt file. Secondly, if you want to speed up the discovery of new pages or updates to existing pages, you can resubmit pages for reindexing on the Google Search Console URL Inspection Tool as covered previously in this article.
Do I Need To Tell Search Engines to Crawl My Website?
By default, the short answer is no, as they will discover your website naturally through backlinks, your sitemap, and if you connected it to Google Search Console or Google Analytics. However, you can speed up this process by manually submitting your sitemap and/or specific URLs for indexing or re-indexing.
Do I Need To Alert Search Engines if I Publish New Content?
Not if your XML sitemap automatically updates. Most CMS platforms automatically update the XML sitemap when new pages are added, modified, or removed.
Can I Get My Page Re-Indexed if It's Been Removed?
If Google has removed your page because it doesn’t meet quality guidelines, then you can modify it using the Webmaster quality guidelines and then submit a reconsideration request to see if the update page has been accepted.
How Can I Stop Certain Pages From Being Indexed?
If you don’t want search engines to index certain pages, then you can add a noindex metatag to the page in the head section, or via your CMS SEO plugin page settings. If the page is already indexed, but you would like to hide it, then you can submit your URL via GSC remove URLs tool.
Hike + Search Engine Indexing
Hike makes it simple to optimize your website for indexing by providing actions to implement that cover any issues found on your website, including problems that may affect the indexing of your website.
If you’re a small business owner or agency that provides SEO services to small businesses, then our platform will help your website get more organic traffic, even if you have little to no SEO knowledge, time, or technical expertise. It’s built for beginners, so make sure to sign up today to start getting more visibility online.