Onsite SEO: Different Ways To Improve SEO on Your Site
What is on-site SEO?
On-site SEO refers to the practices and techniques (see skyscraper technique) used to optimize a website's content and structure to improve its search engine ranking and visibility. The method of optimizing on-site content involves several factors, which include optimizing page titles, meta descriptions, header tags, keyword usage, linking, and other elements that the web administrator has direct control over.
Why is on-site SEO important?
On-site SEO is important because it assists search engines to understand the content and structure of a website, which can lead to improved search engine visibility, higher search engine rankings, and ultimately more organic traffic.
By optimizing on-site website elements, the page content will be more relevant and valuable to firstly - the target audience, and secondly, the search engines. This can help attract more qualified traffic to the site and improve the user experience, which can lead to higher engagement and increased conversions.
On-site SEO can be split into two main categories - content & keywords and other non-keyword on-site factors. Let’s explore both in more detail…
Content & keyword optimization
Most of the on-site SEO factors have to do with the content and keywords, which are broken down into 5 different categories:
Google E-A-T
This acronym, created by Google, stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness, and it is a set of criteria that Google uses to evaluate the quality of a website's content. In other words, it’s a framework that helps Google's algorithms understand whether a website is a reliable source of information on a particular topic.
The E-A-T criteria are important for websites that provide health, financial, or other critical information that may have a significant impact on people's lives.
Websites should ideally provide content that:
Keywords
An important rule to follow when creating pages is to stick with a single, unique topic focus per page. This topic then determines the specific primary keyword that the content is optimized around. Remember to also consider how semantic search works, as it's not just about keywords, it's about the meaning behind the keywords.
In addition to focusing the content around a primary keyword, secondary keywords can be used as support to increase the relevance of the content to the primary keyword. These are often very similar to the primary keyword but phrased differently.
It’s also important to naturally use Latent Semantic Indexing keywords (LSI keywords) throughout the content to provide additional context. These terms and phrases are semantically related to a primary keyword and are not synonyms of the primary keyword, but are related to it in meaning, context, and topic.
LSI keywords are often used by search engine algorithms to identify the relevance and quality of a webpage and to help match it with the search query of a user. By including LSI keywords in content, content creators can help to improve the visibility and ranking of their content in search engine results. You can also let users create content for you, which is called user generated content or UGC.
It's also important to note that the type of keywords can vary, ranging from short-tail keywords (less than 3 words) to long-tail keywords (3+ words), and with the rise of voice search, extra long-tail keywords in the form of questions are becoming more popular, increasing the need for voice search optimization.
Make sure to consider the search intent behind the keywords to determine what the best type of content is for that page.
SEO Writing
Writing copy that is balanced between providing value for the user and optimized for search engines can be a challenge, but the following tips can help focus your content writing efforts so that it provides the best of both worlds:
Readability
Make sure that the content is easy to read and scannable, so users can easily find the information they are looking for on the page without getting lost or confused.
Keep It Concise
Make sure to split up paragraphs and make them only a few sentences long, while focusing on keeping the information as concise as possible.
Avoid Keyword Stuffing
This goes without saying, but keywords should never be inserted for the sake of search engines, but rather should naturally be used within the content so it adds value to the user. In other words, don’t try to over-optimize by adding too many of the same keywords in the content. This also means that keyword density is not used anymore as it was in the past to measure topic relevancy.
Use Headings & Subheadings
Organize your content by structuring it under headings and subheadings, so it makes it easier to scan and find relevant sections within content. This also helps search engines understand your content better as well.
Use Bulleted lists
Not only do bulleted lists make it easier to read & digest content, but it also forces the content writer to be more concise with their thinking. Only use them where it makes sense, such as when having 3 or more items that could be put into an ordered (numbered) or unordered (bullet) list.
Avoid Duplicate Content
Duplicate content should be avoided as it degrades the user experience and confuses search engines which page is the primary one to return in the SERPs. Content that appears in multiple places can be caused mostly by unintentional technical issues, but it can also happen because the content creator is unaware of the harmful effect of having multiple pages with the same or highly similar content. Have a look at how robots meta tags can help noindex certain pages.
Use Tags & Categories Effectively
Tags and categories can be very useful in organizing content on your blog or website, so make sure you understand the difference so you can benefit from using them, especially if you use WordPress or similar CMS.
Content Freshness
Keeping content fresh is also very important as it keeps content up to date with the latest industry updates and encourages visitors to come back for the latest information. Search engines also like this as it means that content is constantly being upgraded and new value being added to improve user experience. Alternatively, try to publish more evergreen content, that isn't affected by short-lived trends. You can also still take advantage of seasonal trends, but you'd need to plan in advance to gain the most advantage here.
Content Gap Analysis
A great way to ensure that you are covering all the best keywords, is to do a content gap analysis with your competitors. This way, you'll be able to see what topics they are missing, which pages you need to create, and thus set yourself up for the best possible success. This process will allow you to find topics you haven't covered yet, but your competitors have, and also hidden opportunities of topics your competitors haven't yet covered.
Avoid Thin Content
Avoiding thin content is essential for improving SEO performance, as search engines favour high-quality, informative content that adds value for users. Thin content often results in poor engagement and higher bounce rates, which can harm a website's search rankings. By prioritizing comprehensive and well-researched content, websites can enhance visibility, attract organic traffic, and create a better user experience, all of which are vital for long-term SEO success.
Visual Elements
Adding visuals such as images, videos, diagrams, charts, or infographics makes content more engaging and splits up chunks of text so it makes it easier to read. Visual elements also give more context to search engines about the page topic and benefit from the image search visibility in Google and other search engines.
HTML Page Elements
There are a few HTML page elements that are important to the on-site content optimization:
Title Tags
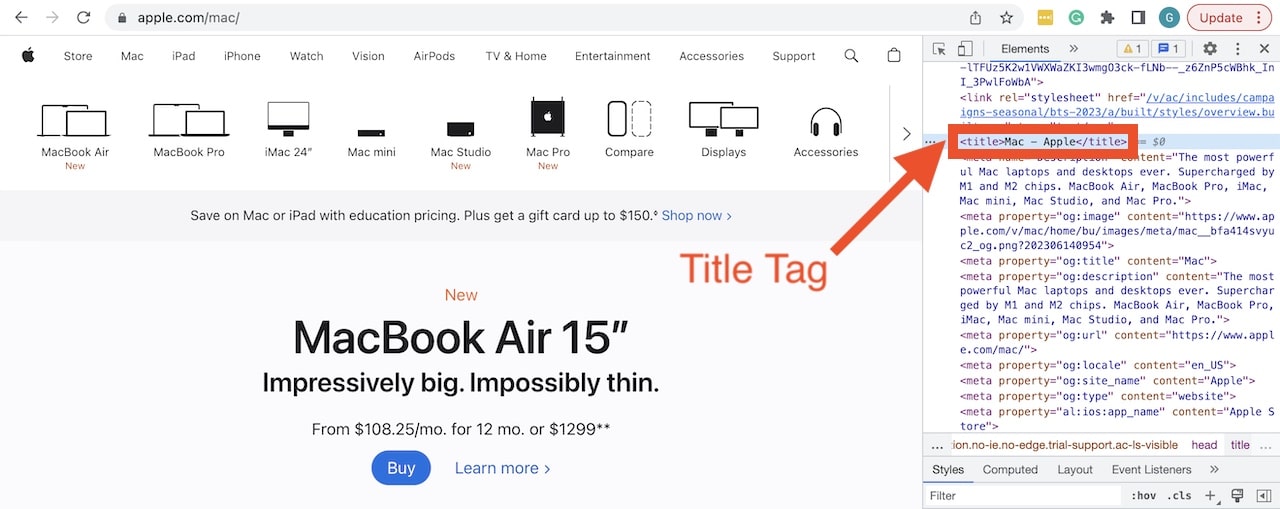
The title tag is an important HTML element that is located on every page (specifically in the head section) and helps search engines to determine the relevance of a page’s topic. In Google, the text in the blue link is the page title that is pulled from the web page.
For example, on Apple's Mac page, you can see the <title></title> tag when you view the HTML source code:
Heading Tags
These are tags ranging from <h1> (H1 tag), <h2> (H2 tag), <h3>, <h4>, <h5>, to <h6> (H6 tag) from highest level of hierarchy to lowest. These heading tags help structure the content into different sections and parts, making it easier to skim and digest. There should only ever be no less than and no more than one H1 tag per page, but there can be more than one of the other heading types.
Read more about SEO heading tags in our more in-depth article.
Meta Description
The meta description tag is also an HTML element that is located on each page and is what Google picks up to use for the search engine results pages as the grey text underneath the blue link. Optimizing the meta description has the potential to increase the click-through rate (CTR), which indirectly affects the search ranking.
When you search on Google, the grey text is the meta description. By default, Google pulls in the first few lines of the body, however, it's always better to define it within your web page settings so it's the right length and grabs attention. Here's an example with the same Mac page:

Image Optimization
Before uploading any images to the website, it’s important to make sure that the images are resized appropriately and are in the most optimal format (jpeg/jpg or webp) before uploading. If you are using other formats like png, make sure to compress it before uploading using a tool like Image Compressor. Many CMS platforms already either have image compression plugins or automatic optimization features, but make sure to check beforehand.
It’s also important to add a descriptive image file name so it can be identified easily - for example, instead of IMG_432.jpg you could call it 5-image-optimisation-tips.jpg if that’s what the image is about.
Finally, once you’ve uploaded the image, make sure to add alt tags (alternative image tags), which are meant to be the text alternative description for visually impaired users and search engines to understand the image content without actually requiring them to see it. Also make sure to add image title tags so anyone hovering over the image can get more context about the image.
Geotagging (local)
If your business is local, then it’s important to optimize content by focusing content on location-specific keywords and including links between other local businesses and organizations. Also, if the business name, address, or phone number (NAP) are mentioned, it’s important to mark these up using Schema Markup (a type of structured data), so that this information can be pulled into the search results as rich snippets.
Other onsite SEO factors
Page Speed
When search engines crawl a website (read the pages & content on a website), they have a certain threshold for how long to wait for a page to load before moving on. The page or site speed, or how many seconds it takes to load a page and its entire contents is very important not to just search engines, but also to user experience.
Having a slow page speed can cause search engine crawling issues as well as increase bounce rates for users that leave the page because it’s taking too long to load.
Many factors affect page speed, but the most important one is image file size. Read the section “Image Optimization” under the “HTML Page Elements” heading for more information. You can also learn what minification is as well as lazy loading and how it helps speed up page loading times.
Responsive Design
In the mobile-first era where most users browse the web using mobile devices, it’s imperative to make sure that websites are designed so that the content is displayed optimally across all devices with varying screen sizes and resolutions.
This ensures a high-quality user experience and makes consuming the content easier. Most CMS platforms have responsive themes, however, it’s still important to double-check. Using Google’s mobile-friendly test allows you to check if a web page is responsive and suits the mobile requirements that are essential to implement.
URL Structure
Organizing content and pages into a logical url structure not only makes it easier for users to navigate your website (see faceted navigation) and find the content they are looking for but also makes it easier for search engines to understand your content and how pages relate to each other. One strategy that can be used to organise your website content effectively is the use of content silos. This strategy refers to the organization of website content into sections or topics. Each section is often created based on keyword research around particular themes.
The content structure will then inform the URL structure based on how many levels deep the hierarchy goes. It also is important to make sure that the URL names are human-readable and are not too long. A URL with 5 words is a good maximum length to cap at. It's also important to use breadcrumbs if you have a multi-level page structure, to allow for easier navigation.
Links
Links, previously called hyperlinks, connect the web and are an essential part of SEO that must be considered when building out a website and the content within it. Internal links create relationships and associations between different sections of content, pages, and websites, helping users to better navigate and discover relevant information and enabling search engines to crawl the website and understand the content from its link profile.
There are three types of links, all of which are important to use within web page content:
Internal
Internal links are links that point to other pages within the same website and are critical for establishing relationships between topics, but also for search engines to be able to crawl the website pages effectively. Each page should ideally have at least 1-2 internal links to other pages of the website if it’s relevant. If a page does not have any internal links, it's considered an orphaned page, which should be avoided.
Outbound
Outbound links are links that point to external website pages, also known as external links, and are also very important to build context around a specific piece of content. By associating to external web pages, it can add value to the user and also show search engines how this page relates to other similar pages, for additional context.
Inbound
Inbound links, more commonly known as backlinks are links on external pages pointing back to your website pages. These links fall under the category of off-page SEO. Inbound links provide authority (both page authority & domain authority) to web pages and domains (see top-level domains) which help to increase search engine rankings.
P.S. Check out the post on redirect chains and difference between 301 vs 302 redirects. Also, if you are considering a website migration, then it's important to review what's involved for the least impact on SEO.
On-site vs Off-site
What is the difference between on-site and off-site SEO?
As explained on this page, On-site SEO is about optimizing your website's content and structure to make it more visible and relevant to search engines. This involves tactics like keyword research, meta tags, and site architecture.
Off-site SEO, on the other hand, involves optimizing external factors that can affect your website's ranking, such as backlinks, social media, and online directories. Strategies for off-site SEO include link building, social media marketing, and online reputation management.
Hike + On-site SEO
Hike can help you with your on-site SEO in the following ways: