301 vs 302 Redirect: SEO Impact & Best Practices
Understanding the difference between 301 and 302 redirects is crucial for effective SEO and user experience. Both serve distinct purposes, with significant implications for search engine rankings and site traffic. This article delves into the nuances of 301 vs. 302 redirects, providing a comprehensive overview of their functionalities, best practices for implementation, and the impact on website performance.
What Are Redirects?
An HTTP redirect is a way for a web server to inform a client that the requested resource has been moved to a different location. When a user or search engine attempts to access a specific URL, the server can respond with a redirect status code, such as 301 (Moved Permanently) or 302 (Found), and provide the new URL where the resource can be found. This is commonly used when a website undergoes restructuring, or when a specific page has been permanently or temporarily moved to a different location. Redirects are important for maintaining a good user experience and ensuring that search engines can properly index and rank web pages.
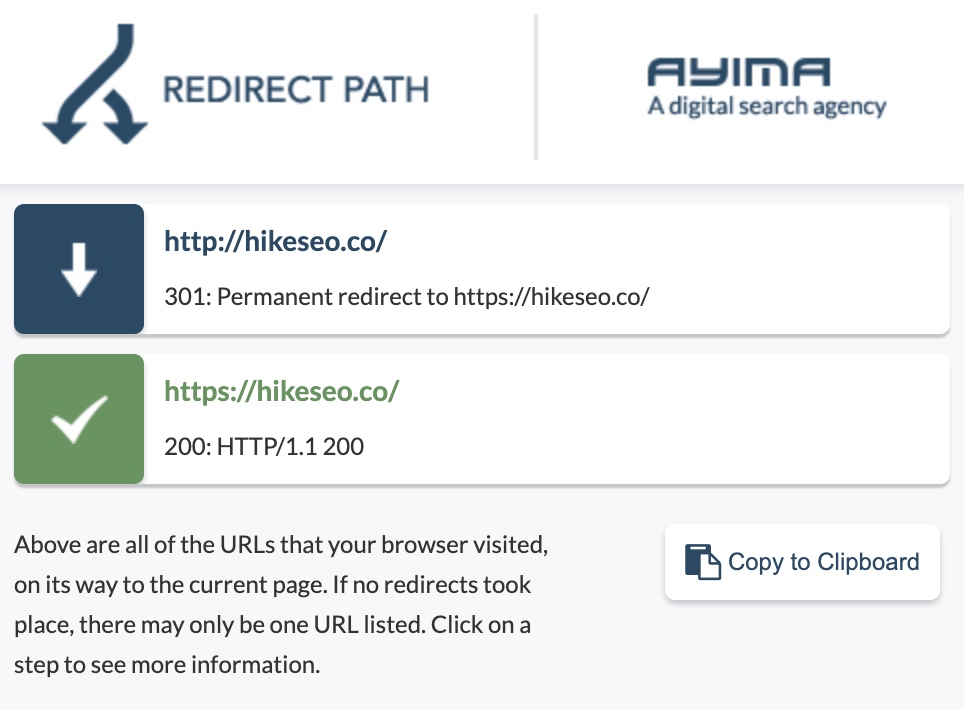
For example, when we visit the non-SSL (HTTP) homepage of Hike SEO, the server redirects us with a 301 redirect to the SSL (HTTPS) version of the page:
Key Differences Between 301 and 302 Redirects
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect, indicating that the original URL has been permanently moved to a new location. It's used when you want to pass on the existing page's authority and ranking power to the new URL. On the other hand, a 302 redirect is a temporary redirect, implying that the move is not permanent and visitors should continue accessing the original URL in future visits.
Impact on SEO
From an SEO perspective, employing a 301 redirect allows search engines like Google to transfer all of the old page’s authority (or "link juice") over to the new one. This means that any backlinks pointing to your old URL will now be attributed to your new destination.
Furthermore, if multiple versions of your website exist (e.g., http://example.com vs https://example.com), implementing proper 301 redirects can consolidate link signals under a single preferred version—preventing dilution of rankings due to duplicate content issues caused by indexing both versions separately.
On the contrary, utilizing a 302 redirect doesn't pass on link equity like its counterpart does with 301 redirects. As such, this type of redirection may not have as significant an impact on SEO efforts because search engines understand that it's only meant for temporary purposes.
Considering these differences in mind can help webmasters make informed decisions about which type of redirection best suits their specific needs.
301 Redirect Use Cases
The primary use case for implementing 301 redirects is during website restructuring or when migrating content between URLs while retaining SEO value. For instance:
1) When merging two websites into one.
2) After deleting obsolete pages but want traffic and backlink value transferred elsewhere.
3) When changing domain names while maintaining previous SEO efforts.
Differentiating Between 301 and 302 Redirects
Technical Differences
From a technical standpoint, search engines treat these two types of redirects differently. When a search engine encounters a 301 redirect, it transfers around 90-99% of link equity from the old page to the new one. In contrast, with a 302 redirect, no link equity transfer occurs as it's considered temporary.
In terms of caching behavior by browsers and intermediate caches, when implementing a 301 redirect, browsers will cache this response indefinitely unless specified otherwise by cache control headers or meta tags. However, for 302 redirects, browsers will not cache them unless specifically instructed to do so.
SEO Consequences
The choice between using a 301 vs 302 redirect can have significant implications for search engine optimization (SEO). Implementing an incorrect type of redirection can impact how search engines index and rank web pages.
Using an appropriate type of redirection is crucial for preserving SEO value when migrating content or restructuring websites. If you want to permanently change URLs without losing SEO value from old links pointing to those URLs, then using a 301 redirect is essential. This ensures that authority and ranking signals are passed on to the new URL.
On the other hand, if you're making changes temporarily or experimenting with different page versions but still want to preserve your existing rankings until you make your final decision, then implementing a 302 redirect would be more suitable.
Implementing 301 Redirects for Websites
When implementing 301 redirects, one common method is to access the website's server and modify the .htaccess file. This file contains directives that tell the server how to behave in certain scenarios, including redirecting URLs. Another method involves using a content management system (CMS) plugin or an SEO tool with a user-friendly interface to set up 301 redirects without directly accessing the server.
A popular technique for implementing 301 redirects is through individual page redirection. This means setting up a redirect for each specific URL that needs to be redirected, ensuring that visitors and search engines are directed to the new page location seamlessly. Some websites use wildcard redirects when they need to redirect multiple pages under one directory or subdirectory.
Importance of Proper URL Redirection
User Experience
Using the correct redirect plays a crucial role. A 301 redirect ensures that users are seamlessly directed to the new page without any disruption or delay. For instance, if a user tries to access an old product page permanently replaced with an updated version, implementing a 301 redirect will automatically take them to the new product page, providing a smooth and uninterrupted browsing experience.
Moreover, from an SEO standpoint, maintaining a good user experience is essential for website rankings. By employing 301 redirects appropriately when content has been relocated or removed, website owners can ensure that visitors are not met with dead ends or broken links. This contributes positively to overall user satisfaction and engagement on the site.
In contrast, 302 redirects indicate temporary moves and may not be as effective in preserving user experience. When utilizing this type of redirection for permanent changes on a website, users might encounter issues such as outdated content still appearing in search results or being redirected back and forth between different URLs unnecessarily.
Search Performance
Proper URL redirection significantly impacts search performance by influencing how search engines index web pages. When implementing 301 redirects for obsolete URLs or outdated content instead of using 302 redirects, websites signal to search engine crawlers that the change is permanent and should be reflected accordingly in their indexes. As a result, link equity (also known as link juice) from the original URL is transferred over to the new one through this type of redirection.
This means that any backlinks pointing to the old URL will pass on their value to the new destination when utilizing 301 redirects effectively. In turn, this helps maintain organic traffic levels even after making significant changes within a website's structure or content hierarchy.
On the other hand, 302 redirects do not transfer link equity as 301s do since they signify temporary moves rather than permanent ones.
Handling Redirect Mistakes in SEO
Common errors can occur, impacting a website's search engine optimization (SEO). One of the most frequent mistakes is using the wrong type of redirect. A 301 redirect is a permanent move, while a 302 redirect is temporary. Misusing these redirects can lead to issues such as loss of traffic and decreased search rankings.
Another error often seen in SEO is failing to update internal links after implementing redirects. When old URLs are not updated with new ones, it can result in broken links and negatively affect user experience. Improper handling of URL parameters during redirection can lead to duplicate content issues, confusing search engines and potentially harming SEO efforts.
Website owners or developers need to be aware of these common errors when dealing with redirects. By understanding the differences between 301 and 302 redirects and being mindful of updating internal links and handling URL parameters correctly, they can avoid detrimental impacts on their site's SEO performance.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting problems related to 301 or 302 redirects involves identifying issues that may arise from incorrect implementation or misuse. One effective troubleshooting method includes utilizing tools like Google Search Console to identify any crawl errors resulting from faulty redirects. This allows webmasters to pinpoint specific pages affected by incorrect redirections.
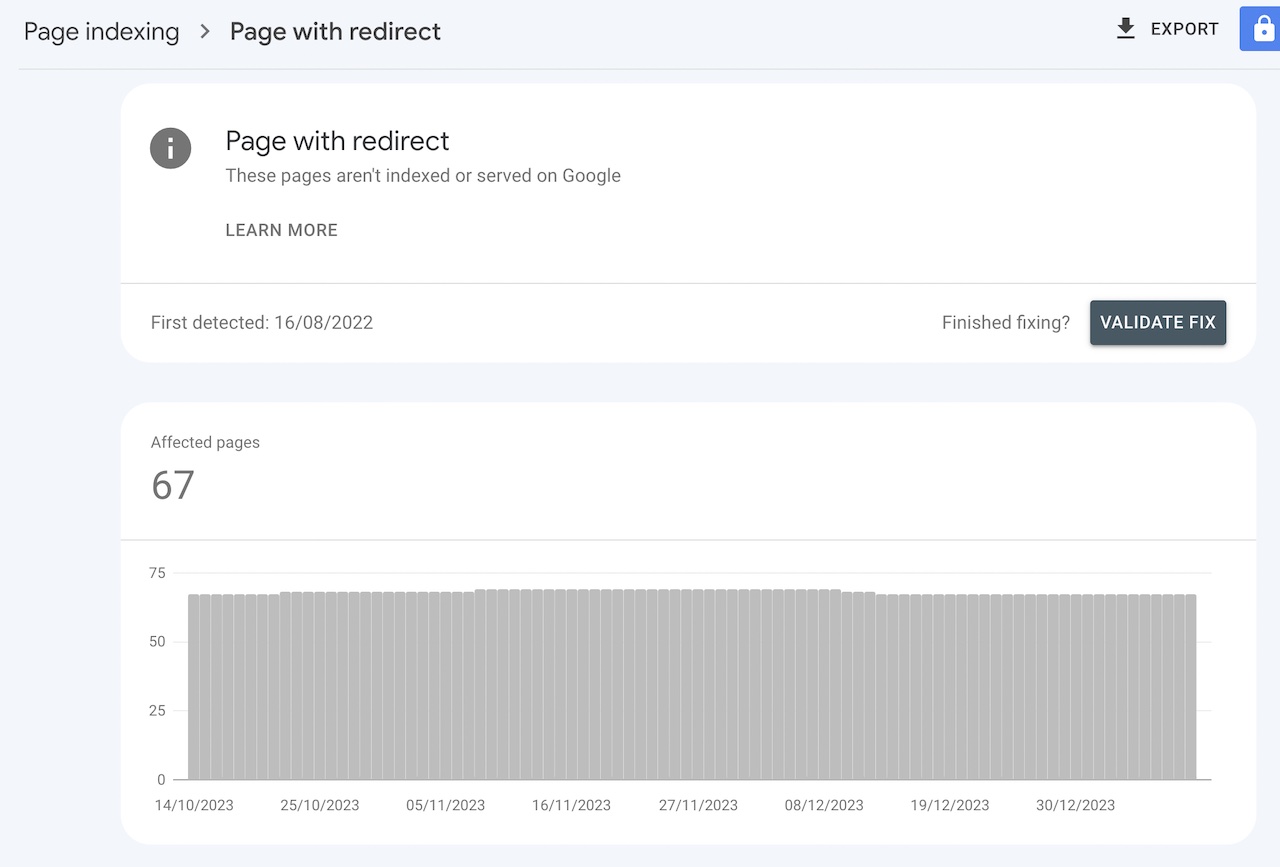
For example, below you'll see that Google Search Console has picked up 67 pages with redirects on a website in the account. Scrolling down, you'll be able to see which pages are affected and take action:
Moreover, conducting regular site audits helps detect broken or outdated internal links caused by improper handling of URL redirections. By reviewing the site structure and identifying areas where old URLs persist without proper redirection, website owners can take necessary corrective actions for maintaining a healthy linking profile.
Staying informed about best practices for implementing URL redirections through reputable sources such as Google Search Essentials ensures that webmasters are equipped with up-to-date knowledge on how to handle various types of redirects effectively.
Significance of Google Aging Delay in Redirection
A key consideration lies in how Google treats each type of redirection. With a 301 redirect, Google typically indexes the new page fairly quickly and transfers most ranking signals from the old page to the new one. However, with a 302 redirect, there's often an "aging delay" where Google continues to display and rank the old URL even after it has been redirected.
This aging delay can be particularly problematic if time-sensitive changes are made on web pages or if outdated content needs immediate replacement by newer versions. Websites may experience prolonged periods during which both old and updated content coexist in search results due to this aging delay caused by improper use of redirects.
Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate potential issues arising from Google's aging delay in redirection, webmasters should prioritize using 301 redirects whenever permanent moves are made within their websites. By doing so, they ensure that ranking signals are accurately passed on to relevant pages without delays caused by outdated indexing.
Regularly monitoring website performance post-redirection can help identify any lingering issues related to aged URLs appearing in search results despite proper implementation of redirects. If such issues arise, submitting updated sitemaps through Search Console can prompt re-crawling and re-indexing by search engines.
Another effective strategy involves proactively managing internal links within websites following major structural changes or content updates alongside implementing proper redirects.
Migrating Websites to New Domains Using 301 Redirects
Planning for website migration involves carefully considering factors such as traffic fluctuations, potential SEO impact, user experience, and long-term goals when choosing between these two types of redirects.
Pros and Cons
Pros of Using 301 Redirects
- Preserves search engine rankings
- Transfers link equity effectively
- Indicates permanent move to new domain
Cons of Using 302 Redirects
- May not pass on link equity efficiently
- Suggests temporary change rather than permanent relocation
Executing this plan may require technical expertise once you've decided on implementing either a 301 or 302 redirect. For websites with multiple pages, it's crucial to ensure that each page is redirected appropriately.
In practice, setting up 301 redirects involves modifying server configurations or utilizing plugins if working with content management systems like WordPress. Each old URL needs to be mapped correctly to its corresponding new URL for visitors and search engines to be seamlessly directed.
For those opting for 302 redirects, similar technical steps need to be taken; however, keep in mind that this type of redirection might not provide optimal results in terms of maintaining SEO value over time.
Monitoring and Testing Website Redirects
Analytics Integration
By adding appropriate redirects, the traffic and engagement data associated with the previous URLs are retained in analytics platforms, providing an accurate representation of user behavior on the new website. For instance, if a business decides to rebrand and change its domain from "oldbusiness.com" to "newbusiness.com," using 301 redirects will help maintain continuity in tracking visitor activity across both domains.
By integrating analytics software, such as Google Analytics, with 301 redirects during website migrations or URL changes, webmasters can effectively monitor and analyze user interactions post-migration. They can track key metrics such as page views, bounce rates, conversion rates, and other valuable insights within their analytics tools. With this information at hand, they can make informed decisions about further optimizing their new website's content structure or addressing any issues arising from the migration process.
Continuous Improvement
By consistently monitoring how users interact with redirected pages through ongoing analysis and testing efforts post-migration using tools like Google Search Console enables webmasters to identify any potential issues arising from redirect implementation promptly. For example:
1) Identifying any unexpected drops in organic traffic.
2) Pinpointing instances where users encounter errors due to incorrect redirection setup.
3) Recognizing opportunities for further optimizing internal linking structures based on user navigation patterns post-redirection.
By continuously refining their approach based on these insights derived from monitoring user behavior after implementing 301 redirects.
Final Remarks
Understanding the nuances between 301 and 302 redirects is crucial for maintaining a website's SEO performance. Implementing proper URL redirection, especially when transitioning from HTTP to HTTPS or migrating to new domains, requires careful consideration of the type of redirect to use. Monitoring and testing website redirects are essential steps in ensuring a seamless user experience and preserving search engine rankings.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a 301 and 302 redirect?
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect used when a page has permanently moved to a new location, while a 302 redirect is temporary and indicates that the move is only temporary. Search engines will pass the ranking power of the old page to the new one with a 301 redirect.
How do I implement 301 redirects for my website?
To implement 301 redirects, you can use server-side directives or plugins if you're using a content management system (CMS). You need to map old URLs to their corresponding new URLs and set up rules in your .htaccess file or server configuration.
Why are proper URL redirections important for websites?
Proper URL redirections are crucial for maintaining SEO rankings, ensuring users reach relevant content, and preventing broken links. They also help search engines understand which version of the URL should be indexed.
How should I handle redirect mistakes in terms of SEO?
If you make mistakes with redirects, promptly fix them by setting up correct redirections. Monitor your website's performance closely after implementing changes to ensure that any negative impact on SEO is minimized.
What is Google aging delay in relation to redirection?
Google aging delay refers to the time it takes for search engines like Google to transfer all ranking signals from an old page to its redirected destination. It's essential because, during this period, both pages may coexist in search results until Google fully recognizes the change.
Hike SEO and Redirects
Hike SEO is an all-in-one SEO platform that allows beginners, small businesses, and agencies to easily and quickly manage & improve their website SEO over time. Hike’s action engine flags up any 404 errors or redirect issues that may have occurred and also guides the user in why it’s important, where it’s happened, and how to fix it.
If you haven’t yet tried Hike, sign up today and see how easy it is to become empowered to take control of your SEO.